Smart Material: Embedded Magneto-Resistive Sensor
Evaluation of (CNT@CIP)-Embedded Magneto-Resistive Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotube and Carbonyl Iron Powder Polymer Composites
by Daeik Jang[1] ,Jae-Eun Park[2] and Young-Keun Kim[2]*
[1] Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, KAIST, 291 Daehak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejoen 34141, Korea
[2] Department of Mechanical and Control Engineering, Handong Global University, 558 Handong-ro, Pohang 37554, Korea
Citation
Jang, Daeik, Jae-Eun Park, and Young-Keun Kim. 2022. “Evaluation of (CNT@CIP)-Embedded Magneto-Resistive Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotube and Carbonyl Iron Powder Polymer Composites” Polymers 14, no. 3: 542. 2022
https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030542
[PDF] View Full-Text
Abstract
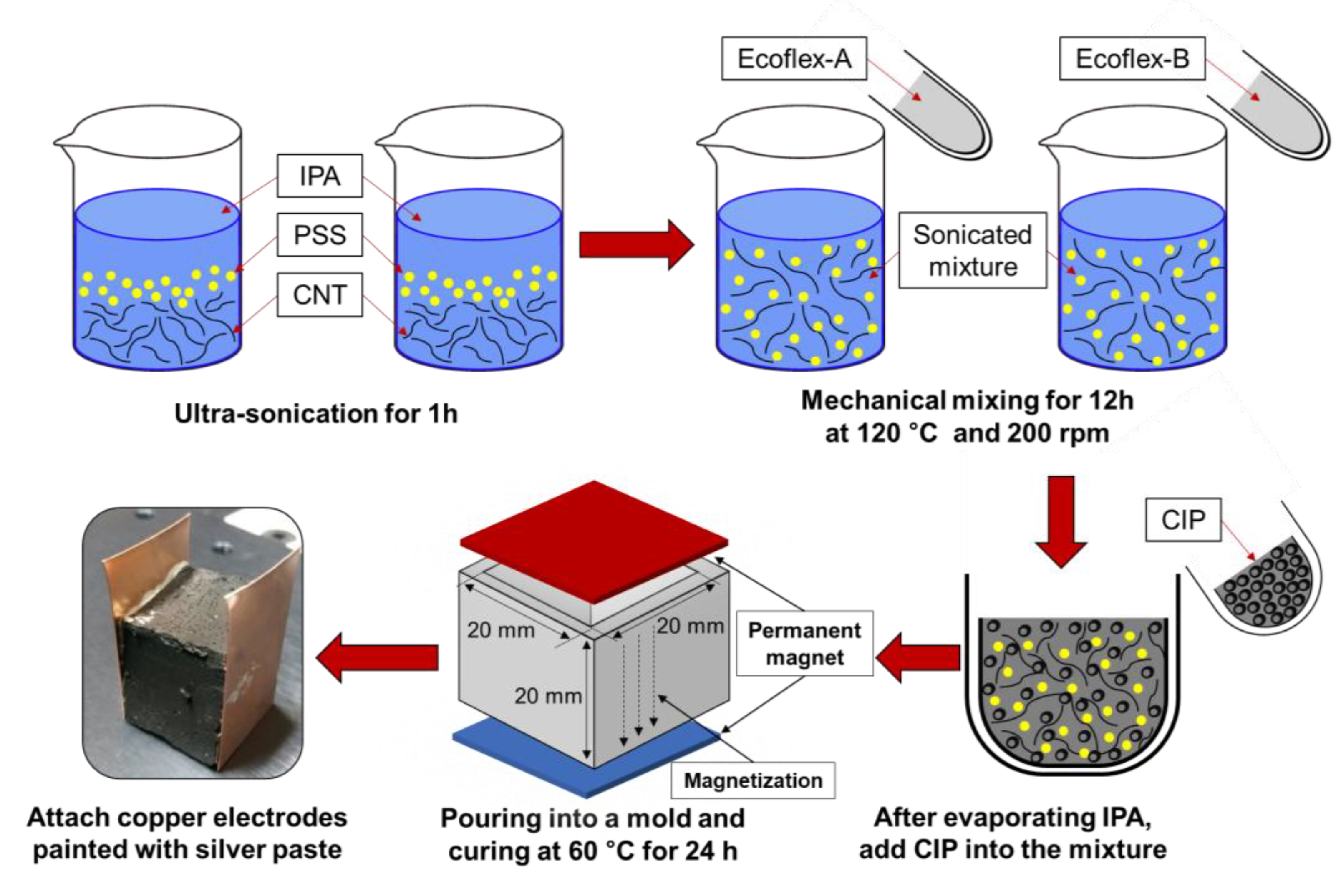
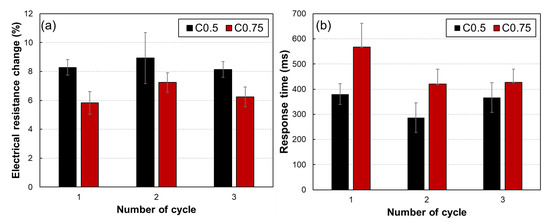
The conductive polymeric composites incorporating carbon nanotube (CNT) and carbonyl iron powder (CIP) have attracted much attention for various sensor applications. In this paper, a comprehensive study of the magneto-sensing property of a CNT-CIP embedded polymer composite is conducted to implement the composite as magneto-sensors. Thus, this study experimentally investigated the magneto-sensing performances of CNT-doped polymeric composites with the addition of CIP in terms of electrical conductivity, sensitivity, repeatability, and response time. First, the CNT-CIP clusters were manufactured and their interactions were analyzed with the zeta potential measurement and SEM observation. Then, the CNT-CIP clusters were embedded into the polymeric composites for the magneto-sensing evaluations. Experiments showed that the CNT contents in the range of percolation threshold (i.e., 0.5% and 0.75%) are optimal values for sensor applications. The addition of CNT 0.5% and 0.75% resulted in a high sensitivity of 7% and a faster response time within 400 ms. Experiment evaluation confirmed a high potential of implementing CNT-CIP composite as magneto-sensors.